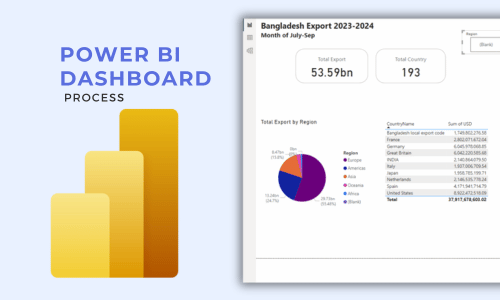
Tutorial on DAX Functions in Power BI
What is DAX?
Data Analysis Expressions (DAX) is a formula expression language. Expression language for
• Power BI.
• Power Pivot for Excel.
• SSAS Tabular Model.
• Azure Analysis Services.
Why DAX?
Designed to support a Larger User Base Simpler than traditional technical languages to learn. Leverage existing knowledge of Excel formulas. Less of a learning curve for Analysts
DAX Functions
- Aggregate Function’s
- Date and Time Functions
- Time Intelligence Functions|
- Filter Functions
- Financial Functions
- Information Functions
- Logical Functions
- Math and Trig Functions
- Relationship Functions|
- Statistical Functions
- Text Functions
- Table Manipulation Functions
- Parent and Child Functions
Aggregate Functions
SUM: Calculates the sum of a column or a set of values.
- Example:
SUM(Table[Column])
- Example:
- AVERAGE: Computes the average of a column or a set of values.
- Example:
AVERAGE(Table[Column])
- Example:
- COUNT: Counts the number of rows in a table or column.
- Example:
COUNT(Table)orCOUNT(Table[Column])
- Example:
- MIN/MAX: Returns the minimum or maximum value from a column.
- Example:
MIN(Table[Column])orMAX(Table[Column])
- Example:
Date and Time Functions
Date and Time functions are useful for working with date and time data in your DAX formulas:
TODAY/NOW: Returns the current date and time.
- Example:
TODAY()orNOW()
- Example:
DATE/YEAR/MONTH/DAY/HOUR/MINUTE/SECOND: Extracts specific components from a date or time value.
- Example:
YEAR([DateColumn])orHOUR([TimeColumn])
- Example:
DATEADD/DATEDIFF: Adds or calculates the difference between two dates.
- Example:
DATEADD([DateColumn], 1, DAY)orDATEDIFF([StartDate], [EndDate], DAY)
- Example:
Time Intelligence Functions
Time Intelligence functions are designed for time-based calculations, especially when working with date tables:
TOTALYTD: Calculates the total for a measure from the beginning of the year.
- Example:
TOTALYTD(SUM(Sales[Amount]), Date[Date])
- Example:
SAMEPERIODLASTYEAR: Retrieves the value from the same period in the previous year.
- Example:
SAMEPERIODLASTYEAR(SUM(Sales[Amount]), Date[Date])
- Example:
Filter Functions
Filter functions allow you to manipulate data based on specific conditions:
FILTER: Filters a table based on specified conditions.
- Example:
FILTER(Sales, Sales[Amount] > 1000)
- Example:
ALL: Removes filters from columns or tables.
- Example:
ALL(Customer[Country])
- Example:
Financial Functions
Financial functions are used for calculations related to finance and investments:
- NPV/IRR: Calculate the Net Present Value and Internal Rate of Return.
- Example:
NPV(DiscountRate, CashFlows)orIRR(CashFlows)
- Example:
Information Functions
Information functions provide information about data types:
- ISBLANK/ISNUMBER/ISTEXT/ISDATE: Checks if a value is blank, a number, text, or a date.
- Example:
ISBLANK([Column])
- Example:
Logical Functions
Logical functions perform logical operations in DAX formulas:
- IF/AND/OR/NOT: Perform conditional statements and logical operations.
- Example:
IF([Sales] > 1000, "High", "Low")
- Example:
Math and Trig Functions
Math and Trig functions perform mathematical and trigonometric operations:
- ROUND/FLOOR/CEILING: Round numbers to a specified precision.
- Example:
ROUND([Value], 2)
- Example:
Statistical Functions
Statistical functions are useful for statistical analysis:
- AVERAGEX/MAXX/MINX: Calculate averages, maximums, or minimums for an expression.
- Example:
AVERAGEX(Products, [Sales])
- Example:
Relationship Functions
Relationship functions help you work with relationships between tables:
- RELATED/RELATEDTABLE: Access related columns or tables.
- Example:
RELATED(Customer[Name])
- Example:
Text Functions
Text functions help manipulate and format text data:
- CONCATENATE/LEFT/RIGHT/MID: Combine text or extract portions of text.
- Example:
CONCATENATE([First Name], " ", [Last Name])
- Example:
Parent and Child Functions
Table manipulation functions allow you to modify and manipulate tables:
- SUMMARIZE/FILTER/ADDCOLUMNS: Create new tables or modify existing tables.
- Example:
SUMMARIZE(Sales, Sales[Product], Sales[Revenue])
- Example:
Table Manipulation Functions
Parent and Child functions are used for working with parent-child hierarchies:
- PATH/PATHITEM: Retrieve paths and specific elements from parent-child hierarchies.
- Example:
PATH(Customer[Name], [Customer Key])
- Example: